 Strengthening your supply chain one link at a time.
Strengthening your supply chain one link at a time.
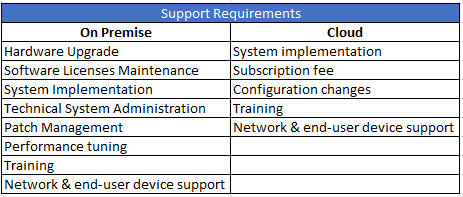
In my experience working with clients to determine the best solution for deploying warehouse automation solutions, the number one IT question is, “Should I deploy the warehouse management system (WMS) on-premise or via the cloud?” Cloud environment upgrades can be overwhelming for clients accustomed to having servers on-premise. Cloud deployments eliminate the need for periodic hardware upgrades and allow continued growth to focus on operations. The cloud solution providers maintain cloud solutions.
What’s the difference between on-premise and cloud?
In terms of scalability, on-premise costs more. Once you scale up, it’s difficult to scale down – which usually leads to heavy losses related to infrastructure and maintenance. On the other hand, the cloud allows you to pay for only what you use – making scale up and down much easier. On-premise server storage usually requires a lot of space, energy, and maintenance. Cloud solution providers (e.g. Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, etc.) maintain the servers, saving you time, money, and space.
What about data security, disaster recovery, and maintenance?
On-premise solutions offer reliable data security since the infrastructure is guarded by not only the security personnel, but also requires authorized access on-site. The only downside is that operational costs can be higher. On-premise security includes firewalls, endpoint security, network security, and hardware security. Alternatively, cloud solutions provide security without you having to monitor and manage security protocols – thus providing some operational cost savings. Cloud security includes API security, cloud workload protection, network security, and code security. In the event of data loss, on-premise solutions can negatively impact the chances of fully recovering all lost data. Robust disaster recovery comes with cloud deployment solutions. From a maintenance perspective, on-premise requires additional software and hardware resources which can be costly. Since cloud solutions are managed by the providers, resource allocation and costs are minimal.
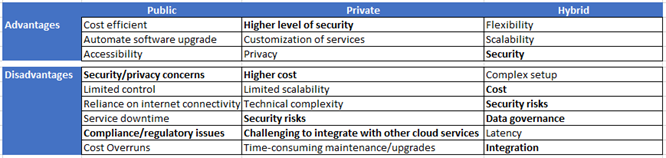
How to choose between public, private, or hybrid cloud?
There are three deployment model types: public, private, and hybrid. With a public cloud, the public can access shared resources like servers, storage, and applications from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. In a private cloud, the infrastructure and services are owned by a single organization, and only authorized users within that organization can have access. A hybrid cloud is a combination of both public and private cloud environments. For instance, some legacy manufacturing companies with mainframe systems and security/data privacy concerns may opt to keep their core back-end services within their own data centers while outsourcing other services (e.g. front-end applications) on the cloud. A hybrid cloud environment would provide accessibility for end users (public cloud) and organizational data privacy (private cloud).
Which cloud service is suitable for you?
Service models include IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. If your business needs a virtual machine, it’s best to use Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). You will be responsible for managing the applications, data, runtime, middleware, and operating system. If your business requires a platform for building software products (e.g. developing, testing, and managing applications), you should choose Platform as a Service (PaaS). You will be responsible for managing the applications and data. If your business wants to be hands-off when it comes to maintenance and IT equipment, you should opt for Software as a Service (SaaS). With SaaS, all software and hardware will be provided and managed by a vendor. SaaS services are highly recommended for clients since it requires less effort.
Choosing a cloud deployment model requires an in-depth understanding of business needs, constraints, and future goals. Cloud deployments eliminate the capital expense of building the server infrastructure and paying overhead to operate your IT environment. Recent studies show that Green IT, or green cloud computing, is becoming more popular due to greater carbon efficiency, increased cost savings, and improved operations efficiency. “Green” meaning environment-friendly and “cloud” meaning the internet. Green cloud computing aims to use technology (SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS) in a way to help improve environmental sustainability by reducing overall power consumption and minimizing the number of servers, switches, cables, etc. Green cloud computing provides resource management (e.g. power/voltage scaling) and sustainable resources (e.g. energy efficient and advanced technology). With the help of green cloud computing, businesses adopt a policy of ensuring that the setup and operations of IT produce a minimal carbon footprint. Ultimately, the shift to the cloud is here to stay.
—Ashley Rhodes, St. Onge Company